by Laura Jones
Updated on March 17, 2025
Did you know that the English present tense isn’t just used to talk about the present moment? It allows you to discuss your life experiences, recent past actions, and even the future! It’s everywhere, whether you’re describing your daily routine, sharing what you’re doing now, or discussing facts.
Many learners struggle with the differences between present simple, present continuous, present perfect, and present perfect continuous, but mastering them can instantly improve your fluency in English. In this article, we’ll break down each type, explain when to use it, and provide clear examples to make learning easier. Get ready to master the tenses that shape everyday communication!
The present tense is used to talk about general truths, habits, things happening now and things that are relevant in the present moment. We also use the present tense to talk about the future. So, how many tenses are there in English? There are 12 major tenses: four present, four past, and four future.
Being able to use the present tenses comfortably is key to becoming a fluent English speaker. If you’re unsure how to learn English grammar, let Lingoda help you. In small group classes, you can learn grammar in a way that is applicable to your daily life. With native-level teachers and a focus on real-life language, you’ll learn to speak with confidence from day one.



Now, let’s take a closer look at the different present tenses and how they shape the way we express ourselves.
The present simple is the most commonly used tense in English. To form the present simple, we use the root form of the verb (often called the base or bare infinitive). This is the form of the verb that is listed in the dictionary. We add -s or -es to third-person singular verbs.
Here are the main ways we use the present simple:
I take Spanish classes twice a week.
The sun rises in the East.
We live in London.
The plane leaves at 7:40.
The second tense we’re looking at is the present continuous. We form this tense with a form of the verb be + -ing verb.
We don’t usually use state verbs in continuous tenses. These are verbs such as love, agree and understand. Here are the main ways we use the present continuous in English:
What are you doing now?
I’m eating lunch at the moment.
They’re renting a flat in New York for a few months.
I’m having dinner with Sally tomorrow at 8.
My tomato plants are growing.
Look at the table to see two uses of the present simple and continuous compared.
| Present Simple | Present Continuous |
| Habits/routines: We watch TV most evenings. | Things happening around the moment of speaking: We’re watching a great program on TV at the moment. |
| Situations we see as permanent: Do you teach geography? | Situations we see as temporary: I usually teach geography, but I’m teaching history this term. |
We use the present perfect tenses to discuss actions that happened or began in the past but are relevant in the present. To form the present perfect simple tense, we use have/has + past participle.
Let’s take a look at some of the main ways we use the present simple tense:
They have tried sushi before.
Oh no, I’ve forgotten my wallet! Do you have any cash?
He’s been a teacher for over 20 years.
Have you seen Alexa this week? (It is still the same week.)
In British English in particular, people often use the present perfect simple to talk about recently completed actions. You’ll see adverbs such as just, already and yet in these types of sentences.
In North American English, people are more likely to use the past tense in these examples. Knowing when to use the present perfect vs. past simple is a challenge for learners.
The present perfect continuous is used to talk about actions that began in the past and are relevant in the present. There is often a focus on the duration of the action. We form the present perfect continuous with have/has been + -ing verb.
Here are 2 of the main ways we use this tense:
It’s been snowing all day. (It’s still snowing)
I’ve been sitting in the sun, and now I’m burned. (I’m not sitting in the sun anymore but the result is that I’m burned now)
Sometimes, there is no difference in meaning when we use the present perfect simple and continuous tenses. Using the continuous tense puts more focus on the duration of the action.
Here is a table showing some of the main differences between the present perfect simple and continuous.
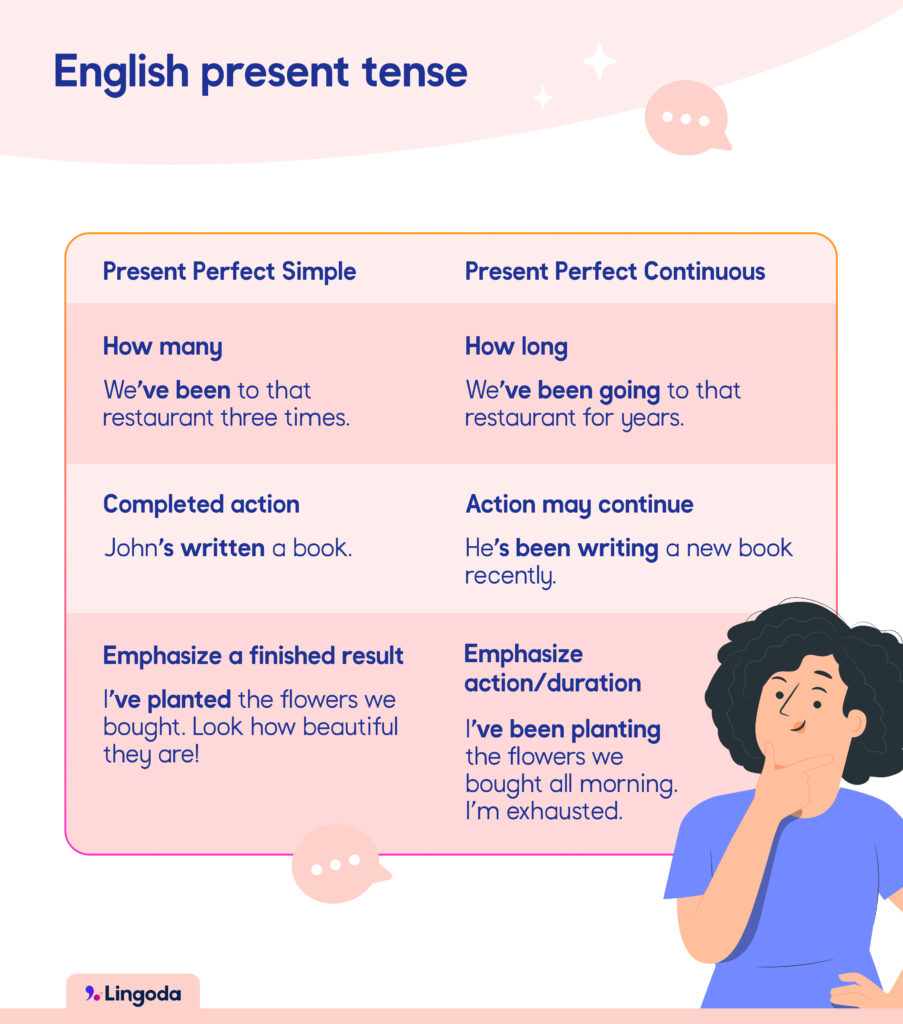
English verbs in the present tense don’t always follow the rules and there are many irregular verbs! In the simple present tense in English, be presents the most problems, as it has three forms: am, are and is. However, a bigger issue arises when you use the present perfect simple. Many verbs have irregular past participles, including very common verbs like be → been, go → gone and do → done. Getting to grips with irregular past participles is key to becoming comfortable using the present tenses.
Another mistake students make often is using stative verbs in continuous tenses. Look at the examples:
One final common mistake is using the present simple or continuous when talking about a time up to now, especially with for and since. Instead, we should use a perfect tense. Here is an example:
English is constantly evolving, gaining new words and seeing older ones take on different meanings. The tenses haven’t stood still, either! If you’ve read works by the famous playwright William Shakespeare, you’ll have seen forms like thou goest (you go) and she hath (she has). Luckily for learners, archaic forms like thou goest have been dropped in favor of simpler structures. Another change is in the the -ing form of verbs, which at one time was spelled –yng, as in castyng, not casting.
The four forms of the present tense are the present simple, present continuous, present perfect, and present perfect continuous.
If you can’t identify the present tense from the form used or the context of the sentence, signal words may help. In the present simple, you’ll see terms like every day, often, sometimes and rarely. In the present continuous, you might see now or at the moment. Sentences in the present perfect simple and continuous often contain such words as since and for, and the present perfect simple often has already, yet, and just. This method isn’t foolproof, so don’t just rely on signal words!
The English present tense has four forms — simple, continuous, perfect, and perfect continuous — each with its own role in expressing habits, ongoing actions, past influences, and future events. Mastering these tenses is key to speaking fluently. If you want to deepen your understanding and gain confidence in using them, learn English with Lingoda. Our expert teachers will help you practice in authentic conversations, ensuring you’re ready to use your new knowledge in the real world.



